What Change Management Is in Safety Management Systems

Change management in aviation safety management systems (SMS) is an extremely important topic. Formal processes to manage change have become important not just for safety performance, but also for demonstrating to SMS auditors that your company knows how to formally manage change as your operations are exposed to changing environmental conditions.
You can bet that poorly managed or documented change management processes will result in an audit finding. The reason is that change management:
- Demonstrates your understanding of the steps in the Safety Risk Management process;
- Shows the quality of your risk analysis activities;
- Validates your ability to document required SMS activities; and
- Bridges the gap between Safety Risk Management and Safety Assurance processes.
Related Articles on Management of Change in Aviation SMS
- What Is Management of Change in Aviation SMS
- Understanding Management of Change in Aviation SMS
- 4 Essential Tips for Management of Change in Aviation SMS
Is MOC Under Safety Risk Management or Safety Assurance?
In aviation SMS guidance materials, we often see management of change (MOC) listed under the either Safety Assurance or Safety Risk Management pillars. Either classification can be true depending on the context of the conversation or the risk management activity.
Regardless of which SMS pillar management of change belongs to, the fact is that change management has increasingly been used and inspected by oversight agencies as a process that very closely resembles the safety risk management (SRM) process, which flows something like:
- Describe the change;
- Identify hazards;
- Identify risks and analyze for credible, worst-case scenarios;
- Assess risks for acceptable level of safety (ALoS);
- Develop new risk controls to process change;
- Evaluate new risk controls for effectiveness;
- Implement new risk controls; and
- Resume monitoring affected systems with new risk controls.
That being said, change management definitely has safety assurance (SA) qualities, which is because it works best when used to bridge the gap between SRM and SA.
Define the SRM Process in Aviation SMS Implementations
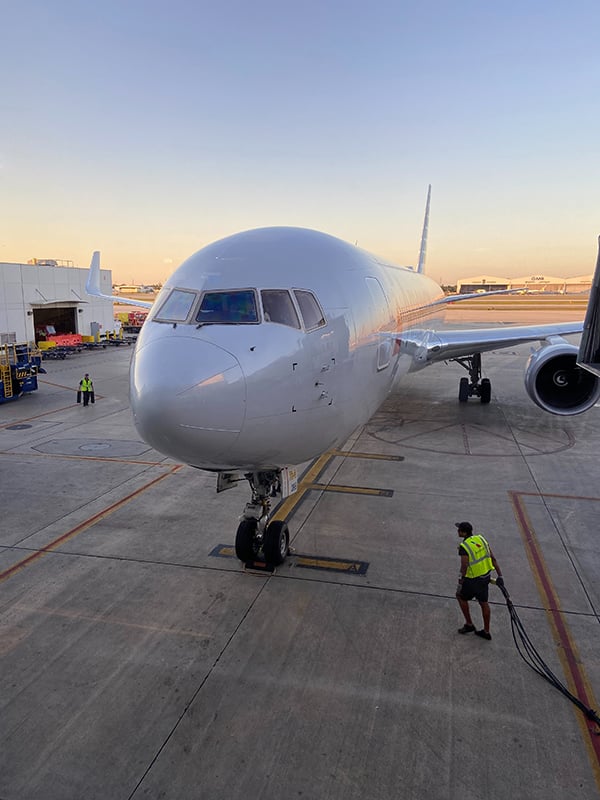

The Safety Risk Management Process in aviation SMS implementations has four distinct goals:
- Identify hazards (old and new);
- Identify risks that are associated with hazards;
- Manage risk controls; and
- Establish and maintain an acceptable level of safety (ALoS).
The basic process of SRM is to:
- Understand a system by describing/outlining it;
- Identify existing and new hazards that can adversely affect operations;
- Identify and analyze risks associated with those hazards;
- Assess credible risk scenarios (with a risk matrix); and
- Develop needed risk controls.
This constant process keeps “SMS implementations on their toes” so to speak. It allows the aviation SMS to adapt to changing conditions by:
- Regularly evaluating risk controls;
- Creating new risk controls when necessary to reduce risk to as low as reasonably practical (ALARP);
- Updating or refining existing controls to meet changing needs;
- Retiring controls that are no long relevant; and
- Communicating change to affected stakeholders.
The end result should be a very high level of documentation that aligns with your "operational risk profile." This overused phrase simply means the “personality” of the area of operations under consideration.
Related Safety Risk Management (SRM) Articles
- 4 Elements of Safety Risk Management (SRM)
- How to Implement SRM Process in Aviation SMS [With Free Checklist]
- Most Important Activities in Safety Risk Management (SRM)
What Are Safety Assurance (SA) Processes in SMS Implementations
The Safety Assurance Process is the monitoring and validation process of SRM. Safety Assurance puts the documentation, controls, and activities of SRM into action. Some common SRM activities are:
- Reviewing, measuring, and monitoring safety data;
- Reporting safety issues and auditing operations;
- Managing safety issues and audit findings;
- Ongoing monitoring of the effectiveness of available management resources (i.e. risk controls) during issue management; and
- Ensuring that program is improving (continuous improvement).
The SA and SRM processes work together in a symbiotic relationship. If the data, safety reporting, and risk management processes are not performing, then the SRM process will be used to make safety changes. These safety changes, in turn, should be naturally validated during the SA process as the affected systems are carefully monitored. This process ensures ad infinitum.
Management of Change Connects SA and SRM Processes
Management of change is an essential link between the SA and SRM processes. MOC helps both processes communicate as a feedback loop in SA processes supports organizational change introduced in the SRM processes. As discussed, the process of change management follows a similar path to SRM. However, the outcomes and results of change management:
- Drive both the SRM and SA processes simultaneously.
To make this clear, change management:
- Follows similar process to SRM;
- Prompts SA monitoring and SRM design activities at the same time.
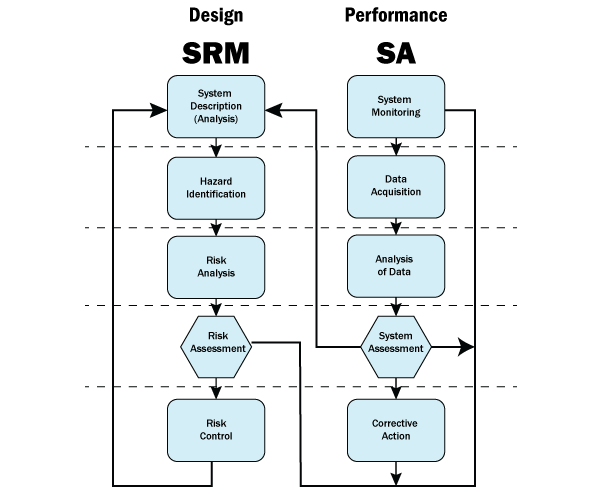
For example, during change management, one of the first activities is to identify hazards (SRM activity). However, in the event that new hazards are found, the outcomes are that:
- These new hazards are usually identified, reported, and managed as safety issues (SA activity); and
- These new hazards are accounted for in the hazard register (SRM activity).
Both of these activities happen at the same time. These exact same outcome activities occur with:
- Risks;
- New risk controls; and
- Additional updates to SMS bureaucracy.
Changes will be analyzed, documented, and accounted for in the process of safety risk management, and monitored with SA activities.
Related Articles on Management of Change in Aviation SMS
- What Are Best Practices for Change Management in Aviation SMS
- 4 Pillars | Most Important Elements of Change Management in Aviation SMS
- 3 Tips for Effective Management of Change Projects in Aviation SMS
Final Thought: Understand Goals of MOC as Bridge for SA and SRM Processes
It’s critical to understand that MOC is an SRM activity that bridges the gap between SA and SRM because:
- Organize separation of concerns, such as accounting for the change (SRM) and monitoring the change (SA);
- Have better organization of change management; and
- Be better able to defend and express change management operations to an auditor.
The third bullet point is especially important. Regardless of the quality of your change management, if an auditor detects any discrepancies, if you can’t quite “remember” why a choice was made, or if you can’t clearly explain your MOC process and how the parts relate to SA and SRM, you can count on a finding.
So be very clear during MOC:
- What you are doing;
- Why you are doing it; and
- How each activity fits into the SA and SRM processes.
If you do this and document well, count on strong audit performance and high-quality change management operations.
Avoid Audit Findings With Management of Change
One of the most common audit findings related to the management of change is the lack of a repeatable process for dealing with the management of change projects. What are your processes to:
- Trigger a MOC project?
- Review related hazards for the change?
- Communicate proposed change with interfacing departments and external organizations?
- Document the organizational review before the change is implemented?
- Monitor the change to validate assumptions?
If your company has trouble answering these questions, or if you have no processes to manage change, then a quick, painless solution is to acquire low-cost, commercially available SMS database software to manage your MOC projects.
An aviation SMS database provides your organization with the necessary tools to effectively manage your safety assurance and safety risk management activities.
These following short demo videos will demonstrate how your company can benefit from a best-in-class SMS database to manage all your SMS documentation requirements.
For more information about performing management of change, you will find these templates helpful:
Do you need tools to effectively manage your safety assurance and safety risk management activities? See how SMS Pro can make you an SMS rock star.
Last updated in December 2025.