What Is Management of Change in Aviation SMS

Management of change in aviation SMS is a formal process for facilitating changes in safety programs. In general, the change management process is evoked when larger, system-level changes are needed in the SMS.
Small changes are handled with corrective actions.
The basic tenants of management of change in aviation SMS are:
- Airlines, airports, and other aviation service providers establish a formal, repeatable process for change;
- All relevant stakeholders are involved in the change;
- All data and safety cases related to the change need to be thoroughly analyzed and assessed; and
- The change is implemented through many smaller changes through the use of corrective preventative actions.
A common strategy for change is to have one manager facilitate the change, and a responsible manager review and approve each stage of the change process as it’s completed.
Importance of Change Management
Change management is complex. It entails that you evaluate the following items in terms of what actually exists, and what is possible:
- Hazards;
- Environments;
- Risks; and
- Operational processes.
Changes may introduce new environments (i.e., new routes), new hazards, new risks, and will certainly entail new processes. As such, change management focuses on real and hypothetical situations.
When these aspects of safety are not analyzed thoroughly enough, organizations are exposed to:
- Unforeseen events;
- Deterioration of risk controls; and
- New hazards and risks that weren’t identified.
Change management also involves every aspect of aviation safety management systems, such as:
- Regulatory changes;
- Organizational restructuring;
- Safety policies and procedures;
- Employee or management changes; and
- Venturing into entirely new operational environments, full of new risks, hazards, etc.
Which of the 4 Pillars Is Change Management Under
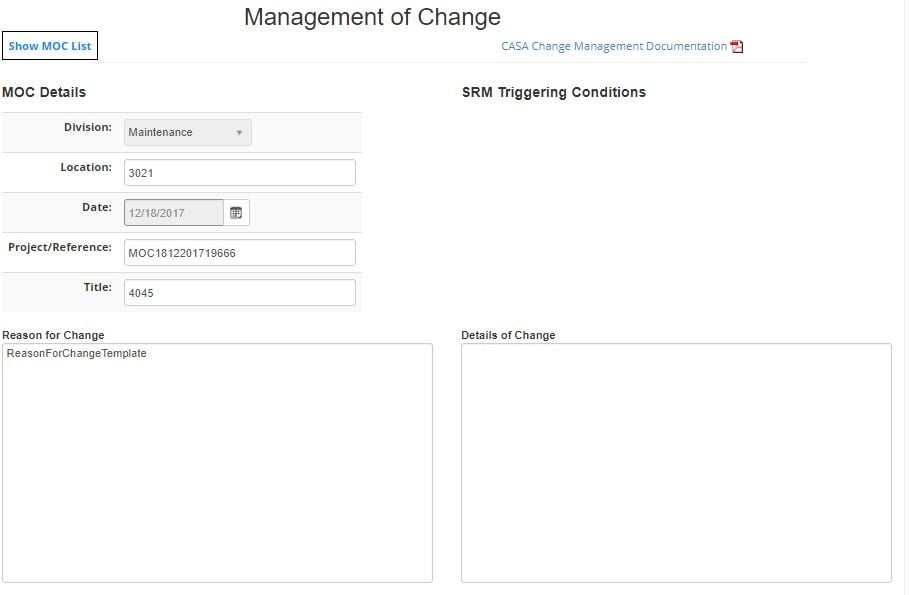
Sometimes you will see management of change listed under the Safety Risk Management pillar (SRM). Sometimes you will see it listed under the Safety Assurance (SA) pillar. So, which of the 4 pillars is change management under?
The quick answer is that management of change is probably the best fit under the SRM pillar, and only barely. However, the real answer is that management of change straddles both the SRM and SA process.
Management of change’s SRM features are:
- Describing the change (i.e., describe the design of the change);
- Identify new hazards and document them;
- Identify new associated risks and analyze them; and
- Evaluate the scope of risk controls.
Change management’s SA features include:
- Implement new risk controls with corrective actions;
- Gather existing hazard data that is relevant to change;
- Perform analysis on all relevant data to change; and
- Evaluate the likely effectiveness of risk controls.
For those of you who are familiar with the SRM and SA interface, you will see that change management encompasses nearly the entirety of this interface.
How to Perform Management of Change in Aviation SMS

Different organizations have different strategies for processing change. We highly recommend processing change through:
- Checklists;
- A series of risk assessments;
- Approvals.
The general workflow for change management looks like this:
- Document the details of the change, the reasons for the change, and the affected parties;
- Identify known hazards that are relevant to the change;
- Conduct hazard analysis to identify new hazards;
- Review risk controls to identify adequate, inadequate, and non-existing risk controls;
- Identify potential compliance requirements;
- Create a list of action items that are needed to implement change, such as action items for training, purchasing, etc.;
- For each action item, create a list of needed tasks to implement changes with corrective preventative actions, thereby completing the action item;
- Implement each CPA; and
- Once implementation is complete, review implementation.
Common side effects of change management are:
- New risk mitigation controls;
- Additional aviation SMS training;
- Communicating the change to employees; and
- Creating a clean audit trail.
What Are Change Management Best Practices
Here are some best practices for performing change management processes:
- How you will be performing the change (i.e., what is your process);
- Why you are performing the change;
- Closely monitor safety culture throughout the change – resistance can kill your change;
- Regularly communicate the change and involve as many relevant employees as possible; and
- Delegate as much as possible, such as by breaking up the change into as many small changes as possible.
Last updated November 2025.